本文环境为Kubernetes V1.11,操作系统版本为 CentOs 7.3,Kubernetes集群安装可以参考kubeadm安装kubernetes V1.11.1 集群 。想要了解更多 Kubernetes 相关知识,可以阅读 Kubernetes 系列学习文章。
容器中的存储都是临时的,因此Pod重启的时候,内部的数据会发生丢失。实际应用中,我们有些应用是无状态,有些应用则需要保持状态数据,确保Pod重启之后能够读取到之前的状态数据,有些应用则作为集群提供服务。这三种服务归纳为无状态服务、有状态服务以及有状态的集群服务,其中后面两个存在数据保存与共享的需求,因此就要采用容器外的存储方案。
Kubernetes中存储中有四个重要的概念:Volume、PersistentVolume PV、PersistentVolumeClaim PVC、StorageClass。掌握了这四个概念,就掌握了Kubernetes中存储系统的核心。我用一张图来说明这四者之间的关系。
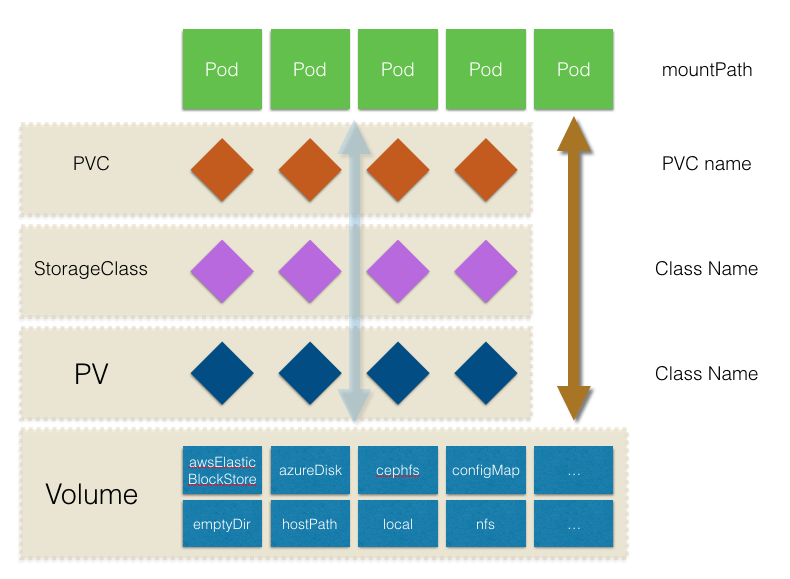
- Volumes是最基础的存储抽象,其支持多种类型,包括本地存储、NFS、FC以及众多的云存储,我们也可以编写自己的存储插件来支持特定的存储系统。Volume可以被Pod直接使用,也可以被PV使用。普通的Volume和Pod之间是一种静态的绑定关系,在定义Pod的同时,通过
volume属性来定义存储的类型,通过volumeMount来定义容器内的挂载点。 - PersistentVolume。与普通的Volume不同,PV是Kubernetes中的一个资源对象,创建一个PV相当于创建了一个存储资源对象,这个资源的使用要通过PVC来请求。
- PersistentVolumeClaim。PVC是用户对存储资源PV的请求,根据PVC中指定的条件Kubernetes动态的寻找系统中的PV资源并进行绑定。目前PVC与PV匹配可以通过
StorageClassName、matchLabels或者matchExpressions三种方式。 - StorageClass。
Volumes
Docker提供了Volumes,Volume 是磁盘上的文件夹并且没有生命周期的管理。Kubernetes 中的 Volume 是存储的抽象,并且能够为Pod提供多种存储解决方案。Volume 最终会映射为Pod中容器可访问的一个文件夹或裸设备,但是背后的实现方式可以有很多种。
Volumes的类型
- cephfs
- configMap
- emptyDir
- hostPath
- local
- nfs
- persistentVolumeClaim
emptyDir
emptyDir在Pod被分配到Node上之后创建,并且在Pod运行期间一直存在。初始的时候为一个空文件夹,当Pod从Node中移除时,emptyDir将被永久删除。Container的意外退出并不会导致emptyDir被删除。emptyDir适用于一些临时存放数据的场景。默认情况下,emptyDir存储在Node支持的介质上,不管是磁盘、SSD还是网络存储,也可以设置为Memory。
1 | apiVersion: v1 |
hostPath
hostPath就是将Node节点的文件系统挂载到Pod中,在之前的例子中也可以看到用法。
1 | apiVersion: v1 |
local
A local volume represents a mounted local storage device such as a disk, partition or directory.
local类型作为静态资源被PersistentVolume使用,不支持Dynamic provisioning。与hostPath相比,因为能够通过PersistentVolume的节点亲和策略来进行调度,因此比hostPath类型更加适用。local类型也存在一些问题,如果Node的状态异常,那么local存储将无法访问,从而导致Pod运行状态异常。使用这种类型存储的应用必须能够承受可用性的降低、可能的数据丢失等。
1 | apiVersion: v1 |
对于使用了PV的Pod,Kubernetes会调度到具有对应PV的Node上,因此PV的节点亲和性 nodeAffinity 属性是必须的。
PersistentVolume nodeAffinity is required when using local volumes. It enables the Kubernetes scheduler to correctly schedule Pods using local volumes to the correct node.
Persistent Volumes
Persistent Volumes 提供了一个抽象层,向用户屏蔽了具体的存储实现形式。
PersistentVolume PV:集群管理员提供的一块存储,是Volumes的插件。类似于Pod,但是具有独立于Pod的生命周期。具体存储可以是NFS、云服务商提供的存储服务。
PersistentVolumeClaim PVC:PVC是用户的存储请求,PVC消耗PV资源。
生命周期:供给
- 静态供给
- 动态供给:动态供给的请求基于StorageClass,集群针对用户的PVC请求,可以产生动态供给。
绑定 Binding
使用
在用对象保护:对于正在使用的PV提供了保护机制,正在使用的PV如果被用户删除,PV的删除会推迟到用户对PV的使用结束。
重用 Reclaim 策略
- 保留 Retain:保留现场,Kubernetes等待用户手工处理数据。
- 删除 Delete:Kubernetes会自动删除数据
- 重用:这个策略已经不推荐使用了,应该使用 Dynamic Provisioning 代替。
扩容。主要是对于一些云存储类型,例如gcePersistentDisk、Azure Disk提供了扩容特性,在1.11版本还处于测试阶段。
PersistenVolume 这个功能目前是通过Plugin插件的形式实现的,目前的版本V1.11.1有19中,特别关注了一下HostPath。HostPath (Single node testing only – local storage is not supported in any way and WILL NOT WORK in a multi-node cluster)
Persistent Volumes 的一些属性
- Capacity:一般情况PV拥有固定的容量
- Volume Mode:在1.9版本中是alpha特性,允许设置 filesystem 使用文件系统(默认),设置 raw 使用裸设备。
- Access Modes
- Class:可以设置成StorageClass的名称。具有Class属性的PV只能绑定到还有相同CLASS名称的PVC上。没有CLASS的PV只能绑定到没有CLASS的PVC上。
- Reclaim Policy
状态
- Available:未被任何PVC使用
- Bound:绑定到了PVC上
- Released:PVC被删掉,资源未被使用
- Failed:自动回收失败
PersistentVolumeClaims
1 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim |
一些属性
- Access Modes
- Volume Modes
- Resources
- Selector:PVC可以通过标签选择器选择PV资源。可以包含两个字段
matchLabels和matchExpressions。 - storageClassName 类似标签选择器,通过storagClassName 来确定PV资源。
Storage Class
StorageClass为管理员提供了一种描述存储类型的方法。通常情况下,管理员需要手工创建所需的存储资源。利用动态容量供给的功能,就可以实现动态创建PV的能力。动态容量供给 Dynamic Volume Provisioning 主要依靠StorageClass。
1 | kind: StorageClass |
